Quad9 Cybersecurity Trends and Insights | February 2023
A Monthly Insight into Quad9’s Top Blocks
In December 2022, Quad9 started publishing a monthly, in-depth report that explores the trending DNS lookups of malicious host names that we blocked during the prior month. Each month, the public will be able to download the entire report, which provides a breakdown of several cybersecurity metrics, including but not limited to the prior month’s highest trending cybersecurity threats by volume of attempted domain access and type.
This information is valuable because it further sheds light on the most prominent malware, phishing, spyware, and botnet threats of which individuals and network administrators should be aware. For Quad9 users, the information in these monthly reports goes beyond supplemental intel surrounding trending cybersecurity and privacy threats. They also serve as peace of mind that Quad9’s public and free DNS service is helping to protect users with a safer, more private online experience.
Quad9 Identified Cybersecurity Threat Trends – January 2023 Data
Last month, Quad9 observed a diverse array of threat categories. Among the many categories of threats blocked and analyzed, the top three were malvertising, information stealing, and DDoS threats. The graphic below represents Quad9’s identified malware trends by threat category during January 2023 — all of which were blocked by Quad9.
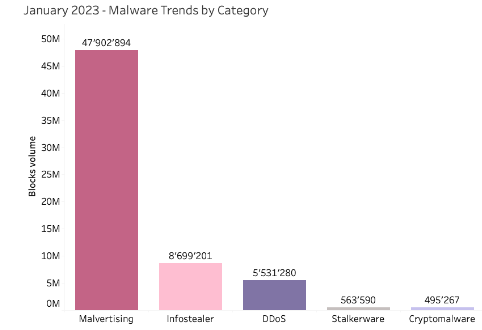
The graph above represents malware trends observed and blocked by Quad9 during January 2023. Due to the volume of DNS requests, Quad9 does not collect all the DNS requests, thus analyzed samples were recorded daily for the duration of 60 seconds each hour. It should be noted that Quad9’s methodology was changed this month to improve the quality of data. Source: Quad9.net
During January 2023, the threat type with the highest volume of observations and blocks was malvertising. Observations of this threat type have become increasingly common in recent months. According to the Center for Internet Security, malvertising is the practice of injecting malicious code in otherwise legitimate ads which are then distributed across advertising networks. Once an infected ad — which are exceptionally difficult for advertising networks to identify — is displayed on a partner website, users of that website become vulnerable to the malicious code embedded in the ad. Typically, an infected user’s machine connects to a server responsible for hosting various exploit kits. Once executed, these exploit kits attempt to identify vulnerabilities on the user’s machine. These exploit kits are often associated with malware that can grant admin access to an infected machine, mine for sensitive data, execute ransomware, or connect the user’s machine to a botnet. [Source].
Among the observed and blocked domains associated with malvertising, the Omnatuor Malvertising Network was most prevalent during January 2023, with an observed 16.5 million queries to omnatuor[.]com.
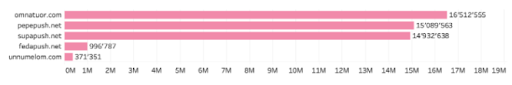
Source: Quad9.net – January 2023 malvertising network observations and blocks by domain
The Omnatuor malvertising campaign targets and compromises vulnerable WordPress websites through embedded malicious JavaScript or PHP code. Once in place, the code redirects users to view and click malvertisements through pop-ups and push notifications. [Source]
The second highest volume threat type observed and blocked during January 2023 by Quad9 was infostealer threats, primarily by the JavaScript threat, ViperSoftX. This multi-stage cryptocurrency stealer is typically spread via torrents and file-sharing sites. First observed in 2020, ViperSoftX’s presence has grown significantly. This malware targets Windows systems, deploying a Google Chrome extension named “VenomSoftX”. Quad9 observed multiple domains generated using a domain-generating algorithm (DGA) which were also reported by threat researchers [Source]. Notably, among the top 100 domains blocked by Quad9 during January 2023, 31 were referenced by ViperSoftX’s dropper.
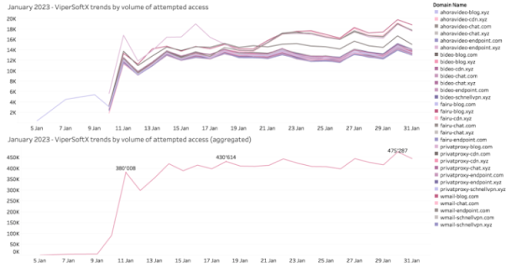
Source: Quad9.net – January 2023
As expected, based on historical trends, the volume of DDoS attack vectors continued to grow during January 2023, with Fodcha and Chaos retaining the 1st and 2nd highest volume of observations and blocks within this malware family.
Continuing the trend from previous months, fridgexperts[.]cc was identified as the domain with the highest number of blocks within the DDoS malware family. This domain is attributed to Fodcha Command and Control (C2) server. Fodcha Command remains a relatively new, yet powerful DDoS botnet, discovered by 360 Netlab researchers in April 2022. This DDoS botnet has caused quite a stir within the cybersecurity community, as researchers report the latest version having grown to an unprecedented scale.
The domain associated with Chaos malware, which is a predecessor to Kaiji malware [Source], was ars1.wemix[.]cc. Chaos is a multifunctional malware that targets Windows and Linux systems as well as Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Although the volume of attempted access for DDoS-related domains was lower during January 2023, Quad9 observed a large spike in attempts earlier in the month for Chaos malware.
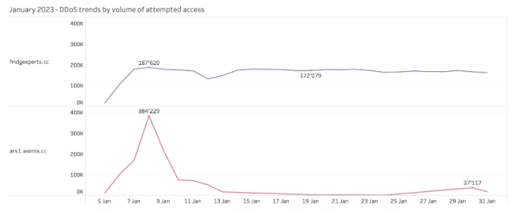
Source: Quad9.net – January 2023
Stalkerware threats continued to increase during January 2023. Stalkerware applications are a form of spyware that can record a user’s conversations, locations, and device input (keylogging). This type of spyware is often done under the guise of a legitimate application.
Based on Quad9’s Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) research, the programs communicating with ixhtb.s9gxw8[.]com are often downloaded from untrusted sources in the form of Android applications, frequently masked as fake games such as Flappy Bird or Apex Legends [Source]. Quad9’s observation of a constant volume of attempted access throughout January 2023 suggests that many Quad9 users have unwanted programs running on their Android devices.
The Takeaway
Quad9’s mission is to improve the security and stability of the internet, creating an ecosystem where users are less vulnerable to risks and more effective in their daily online interactions. By preventing connections to known malicious sites, Quad9 reduces exposure risks before they are downloaded to a device or before potential victims gain access to fraudulent websites.
Access the full report.
References:
4. https://blog.lumen.com/chaos-is-a-go-based-swiss-army-knife-of-malware/
5. https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AssoEchap/stalkerware-indicators/master/generated/hosts